

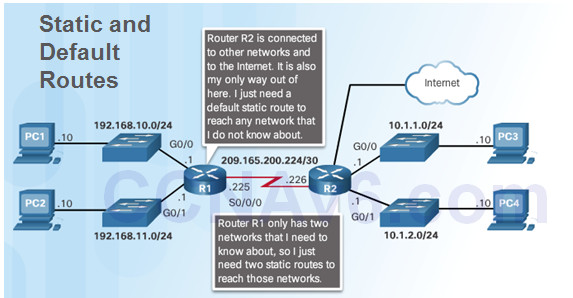
So the default entry that says any unknown destination, send it this way through router A, in this example, is going to be enough. You know that all of them are outside and all of them are simply reachable through that one link. You do not really want to know the specifics of which destinations you want to reach. The Internet is a perfect example of this. It is on those scenarios of stub networks like the one in the figure with a single link into the rest of the network, that static routing is a suitable answer.įor upstream traffic, leaving the stub network, a special case of static route, the default route is typically used to forward all traffic to all destinations outside of the stub network. How fast you adjust and how fast you converge to learning or selecting a different path, that depends on the routing protocol. With dynamic routing protocols, then you have the overhead of advertising and learning networks, but you will adjust the network changes. However, they are static and so the router will not adjust to network changes, if you use static routing. They are fairly simple to configure and if you remain within a certain limit in terms of the number of static routes, then they are very flexible. Static routes do not add overhead in the form of routing protocols, advertisements, and extra intelligence on the routers. In some scenarios like stub networks or locations with a single link into the network or even Internet connectivity, static routing is also an option. Dynamic information also includes destinations learned via routing protocols. This is dynamic because if the directly connected interface goes down, then router will adjust and remove that destination from the routing table. That intelligence of the topology and changes in the topology are maintained statically or dynamically.ĭynamic information includes connected networks, which the router knows and is able to insert in the routing table. Routers will maintain intelligence of the network topology and forward packets based on destinations, selecting the best path across that topology. Router OperationsĪt this point, we know what the routing function is all about. You will then get a chance to configure and monitor static routes on IOS routers by using the command-line interface, including special cases like default routes. We will compare and contrast static versus dynamic routing and highlight the benefits and drawbacks of each option.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
